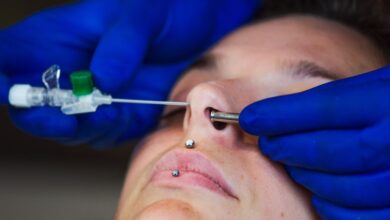
A nose piercing is a stylish and expressive form of self-adornment — but without proper care, it can easily become irritated or infected. Cleaning your piercing correctly is essential to prevent bacteria buildup, swelling, or scarring. This guide walks you through the safest, most dermatologist-approved ways to clean your nose piercing at home and keep it looking great.
How to Clean a Nose Piercing
1. Wash Your Hands First — Always
Before touching your piercing, wash your hands with antibacterial soap and warm water. Dirty hands can transfer bacteria directly into the piercing site, increasing your risk of infection.
Avoid using alcohol-based sanitizers right before cleaning, as they may irritate freshly pierced skin.
2. Use a Sterile Saline Solution
The safest and easiest way to clean your piercing is with a sterile saline solution.
You can buy pre-made saline sprays at pharmacies or make your own by mixing:
-
¼ teaspoon of non-iodized sea salt
-
with 1 cup (240 ml) of warm distilled water
Use a clean cotton pad to gently apply the solution to both sides of your piercing twice daily.
💡 Tip: Avoid hydrogen peroxide or alcohol — they’re too harsh and can delay healing.
3. Gently Remove Crust or Debris
During healing, it’s normal for a bit of crust to form around your piercing. Use a soaked cotton swab to gently loosen and remove any dried discharge.
Do not pick at it with your fingers, as this can cause bleeding or reopen the wound.
4. Avoid Over-Cleaning
Cleaning too frequently can irritate your skin and slow healing.
Stick to 2 times a day — morning and evening — and avoid twisting or turning the jewelry excessively.
5. Keep Makeup and Lotions Away
Until your piercing is fully healed, avoid applying foundation, lotion, or skincare products directly around the piercing site. These products can clog pores or introduce bacteria.
If makeup is unavoidable, use hypoallergenic and non-comedogenic products, and clean gently afterward.
6. Be Patient — Healing Takes Time
Nose piercings can take up to 6 months to fully heal, depending on placement and aftercare.
Continue cleaning consistently, avoid swimming in pools or hot tubs, and never remove the jewelry too early.
When to See a Doctor
If you notice severe redness, pus, swelling, or pain that worsens, consult a dermatologist or piercing professional immediately — you might be dealing with an infection.
Conclusion
Keeping your nose piercing clean doesn’t have to be complicated — consistency, gentle care, and the right products make all the difference. By following these simple steps, you’ll reduce infection risks and enjoy a beautifully healed piercing for years to come.
Suggested Internal Links
-
How to Treat an Infected Nose Piercing: 5 Tips to Follow
-
Best Aftercare Products for Piercings: What Really Works
-
Foods That Help Your Skin Heal Faster